The main lesson of this year’s transfer window
is that UEFA’s Financial Fair Play (FFP) rules have a true bite (no pun
intended). Surely, the transfer fees have reached usual highs with Suarez’s
move to FC Barcelona and Rodriguez’s transfer from AS Monaco to Real Madrid and
overall spending are roughly equal to 2013 (or go beyond as in the UK). But clubs sanctioned under the FFP rules
(prominently PSG and Manchester City) have seemingly complied with the
settlements reached with UEFA capping their transfer spending and wages.
FFP's Transfer Diet
PSG’s
summer of impuissance
It was widely expected, and trumpeted, that PSG
and Manchester City would disregard the transfer restrictions imposed on them. Besides
all the talking and the costly recruitment of David Luiz for nearly 50M€
earlier this summer, PSG’s transfer activity was limited to Serge Aurier’s
arrival on loan from modest Toulouse. Moreover, the talks over Di Maria’s move
to PSG faltered over the inability of the French club to pay a
transfer fee due to the FFP constraints. Thus, PSG was forced into relative thrift by the FFP rules, a
remarkable achievement in itself. This has recently triggered widespread critique against UEFA and FFP by PSG officials.
Manchester City overtaken by Manchester United
Even though Manchester City has largely
dominated the transfer contest against its arch-rival over the latest years,
this balance has dramatically tilted during this summer. United was able to
attract a number of high-ranked and expensive players, most notably Di Maria
for the total sum of 66M€ (more than City’s total spending). In a final
transfer twist, United was even able to snap away Falcao from City apparently due to FFP concerns. City did
not engage in the usual frenzy spending spree of the previous years. It did
spend around 60 M€ (and racked in 25M€ in transfer fees), but this number pales
in regard to the 116M€ spent in 2013. Here again, despite talks to the contrary
and vouching to disregard UEFA’s FFP rules, one cannot ignore the toll taken by
them on the capacity of Manchester City to outrageously dominate the
UK transfer market.
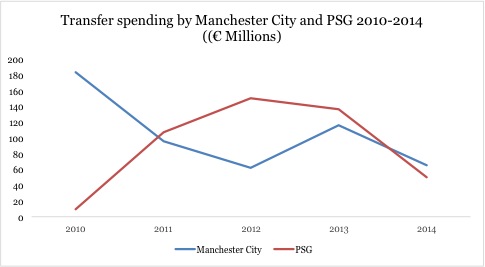
The
general timidity of FFP culprits
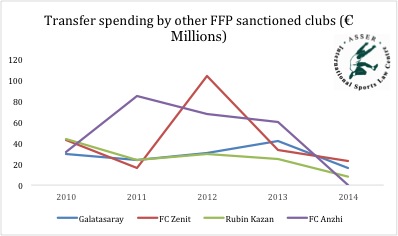
This is not an isolated development. Other
clubs concerned by FFP settlements have followed a similar path (see graph below).
In general, clubs sanctioned under FFP rules have reduced their transfer spending
in comparison to previous years. More surprisingly, big players like PSG and
Manchester City have complied with the net transfer limit of 49M€ imposed on
them in the settlement. This points at an apparent success of the FFP
regulations, which have not materialised, as many feared, as a public relations exercised in the guise
of a toothless regulation. The rules have a real-world impact, and in spite of
the high profiles of certain clubs concerned those have felt the urge to
internalize them reinforcing UEFA’s claim that FFP is a serious regulation. As
will be shown below, however, this also supports the claims that FFP
regulations constitute a restriction on competition in need of adequate
justification.
New strategies to bypass FFP rules
This development has also led clubs to devise bypassing
strategies to the FFP rules. The first strategy is to use loans as temporary or differed transfers by
including a mandatory transfer clause in the contract. This is the solution
adopted by PSG in the transfer of Serge Aurier from Toulouse. In a way there is
no reason why this should not be considered as a new liability for accounting
purposes, as it is akin to a delayed payment but not to a delayed transfer.
Finally, there is the possibility of using affiliated clubs to store the
long-term liabilities (wages and fees), while getting a player on short-term
loans. This is likely the strategy used by Manchester City in the now infamous
recruitment of Frank Lampard from its sister club New York City FC. Hence, one
should not underestimate the ability of clubs to sidestep the FFP rules, albeit
a way more difficult and protracted transfer game as before.
FFP’s compatibility with EU competition law
still a threat
Does this real-world efficacy change anything to
the assessment of FFP’s compatibility with EU competition law? Not really. On
the one hand, it is all the more evident that the FFP rules have a restraining
effect on free competition; certain economic actors are undoubtedly not free to
invest their money, as they would see fit. On the other hand, the real test for
evaluating the FFP’s compatibility with EU law is the Wouters/Meca-Medina
proportionality test developed by the EU Court. First of all UEFA will have to
identify the legitimate objective it intends to pursue with these regulations.
This is likely to be good corporate governance, as one cannot consider that FFP
rules improve the competitive balance by reducing the inequality between clubs in
the absence of any redistributive effects. Actually, FFP will most likely
sclerotize the pre-existing hierarchies. If good corporate governance in
football is deemed a worthy objective (it probably will), the next question
will be: are these regulations a proportionate mean to achieve it? At this
stage UEFA will need to explain why the existing national bankruptcy frameworks
are inadequate for this purpose (due, for example, to the political influence
of clubs like in Spain, or to the particular feature of football competition that
cannot tolerate the vagaries of a normal bankruptcy process), but also why the
existing debt stock is not taken into account by the rules. Here, the brunt of
the socio-political debate on the need of FFP will unfold.
As UEFA’s FFP rules strengthen their grip over
clubs, they will be more and more incentivized to contest the rules in front of
the EU Commission (PSG and Manchester City fans have recently submitted a complaint) or national tribunals. Thus,
these questions will not remain hypothetical and will have to be met by UEFA
with hard facts and convincing arguments. If not the FFP rules will be
remembered as an ephemeral, though remarkable, interlude of the summer 2014.
|
Clubs
|
Amount
spend on transfers in 2010 (in millions)
|
2011
|
2012
|
2013
|
2014
|
|
Manchester City
|
€182.45
|
€96.05
|
€61.95
|
€116.0
|
€65.5
|
|
PSG
|
€9.0
|
€107.1
|
€149.45
|
€135.9
|
€49.5
|
|
Galatasaray
|
€29.5
|
€23.6
|
€30.05
|
€41.84
|
€15.75
|
|
Trabzonspor
|
€7.9
|
€24.45
|
€8.06
|
€4.7
|
€29.11
|
|
Bursaspor
|
€1.38
|
€10.2
|
€3.66
|
€2.33
|
€1.8
|
|
FC Zenit
|
€43.0
|
€16.2
|
€103.76
|
€32.8
|
€22.8
|
|
Rubin Kazan
|
€43.6
|
€23.35
|
€29.0
|
€25.1
|
€8.0
|
|
FC Anzhi
|
€31.2
|
€84.5
|
€67.9
|
€59.4
|
€0
|
|
Levski Sofia
|
€0.8
|
€0.95
|
€1.25
|
€0.59
|
€0.05
|
Data from transfermarkt.com