Editor's note: Marine Montejo is a graduate from the College of
Europe in Bruges and is currently an intern at the ASSER International Sports
Law Centre.
Part 2. EU competition law and sports funding
The first analysed impact of Brexit on
sport was the one regarding EU internal market rules and free movement.
However, all sport areas that are of interest to the European Union will be
impacted by the result of the future Brexit negotiations. This second part of
the blog will focus on EU competition law and the media sector as well as
direct funding opportunities keeping in mind that if the UK reaches for an EEA
type agreement competition law and state aid rules will remain applicable as
much as the funding programs. More...
Editor’s note: This report
compiles all relevant news, events and materials on International and European
Sports Law based on the daily coverage provided on our twitter feed @Sportslaw_asser. You are invited
to complete this survey via the comments section below, feel free to add links
to important cases, documents and articles we might have overlooked.
The Headlines
This month saw the conflict between FIBA Europe
and the Euroleague (more precisely its private club-supported organizing body,
Euroleague Commercial Assets or ‘ECA’) becoming further entrenched. This
dispute commenced with FIBA creating a rival Basketball Champions League, starting from the 2016-2017 season with the hope to reinstate their
hold over the organization of European championships. The ECA, a private body
that oversees the Euroleague and Eurocup, not only decided to maintain its
competitions but also announced it would reduce them to a closed, franchise-based league following a
joint-venture with IMG. In retaliation, FIBA Europe suspended fourteen
federations of its competition (with the support of FIBA) due to their support for the Euroleague project.More...
Editor’s note: Marine Montejo
is a graduate from the College of Europe in Bruges and is currently an Intern
at the ASSER International Sports Law Centre.
In its decisions regarding the joint selling of football media rights (UEFA, Bundesliga, FA Premier
league), the European Commission insisted that premium media
rights must be sold through a non-discriminatory and transparent tender
procedure, in several packages and for a limited period of time in order to
reduce foreclosure effects in the downstream market. These remedies ensure that
broadcasters are able to compete for rights that carry high audiences and, for
pay TV, a stable number of subscriptions. In line with these precedents, national
competition authorities have tried to ensure compliance with remedy packages.
The tipping point here appears to be the premium qualification of sport rights
on the upstream market of commercialization of sport TV rights.
This begs the question: which sport TV rights must be
considered premium? More...
On
the first of May 2015, the Spanish Government finally signed the Royal Decree
allowing the joint selling of the media rights of the Spanish top two football
leagues. The Minister for Sport stated that the Decree will allow clubs to “pay
their debts with the social security and the tax authorities and will enable
the Spanish teams to compete with the biggest European Leagues in terms of
revenues from the sale of media rights”.[1]Although
the signing of the Royal Decree was supposed to close a very long debate and
discussion between the relevant stakeholders, its aftermath shows that the Telenovela is not entirely over.
This
blog post will first provide the background story to the selling of media rights
in Spain. It will, thereafter, analyse the main points of the Royal Decree and outline
how the system will work in practice. Finally, the blog will shortly address
the current frictions between the Spanish League (LFP) and the Spanish football
federation (RFEF).More...
The selling of media rights is currently a hot
topic in European football. Last week, the English Premier League cashed in
around 7 billion Euros for the sale of its live domestic media rights (2016 to
2019) – once again a 70 percent increase in comparison to the previous tender. This
means that even the bottom club in the Premier League will receive
approximately €130 million while the champions can expect well over €200
million per season.
The Premier League’s new deal has already led
the President of the Spanish National Professional Football League (LNFP),
Javier Tebas, to express his concerns that this could see La Liga lose its position as one of Europe’s leading leagues. He reiterated
that establishing a centralised sales model in Spain is of utmost importance,
if not long overdue.
Concrete plans to reintroduce a system of joint
selling for the media rights of the Primera
División, Segunda División A, and la
Copa del Rey by means of a Royal Decree were already announced two years
ago. The road has surely been long and bumpy. The draft Decree is finally on
the table, but now it misses political approval. All the parties involved are
blaming each other for the current failure: the LNFP blames the Sport
Governmental Council for Sport (CSD) for not taking the lead; the Spanish Football
Federation (RFEF) is arguing that the Federation and non-professional
football entities should receive more money and that it should have a stronger
say in the matter in accordance with the FIFA Statutes; and there are widespread rumours that the two big earners, Real Madrid and FC Barcelona, are actively
lobbying to prevent the Royal Decree of actually being adopted.
To keep the soap opera drama flowing, on 30 December 2014, FASFE (an
organisation consisting of groups of fans, club members, and minority
shareholders of several Spanish professional football clubs) and the
International Soccer Centre (a movement that aims to obtain more balanced and
transparent football and basketball competitions in Spain) filed an antitrust complaint with the European Commission against the LNFP. They
argue that the current system of individual selling of LNFP media rights, with
unequal shares of revenue widening the gap between clubs, violates EU
competition law.

Source:http://www.gopixpic.com/600/buscar%C3%A1n-el-amor-verdadero-nueva-novela-de-televisa/http:%7C%7Cassets*zocalo*com*mx%7Cuploads%7Carticles%7C5%7C134666912427*jpg/
More...
Our first report on the FIFA business dealt with FIFA’s revenues and highlighted
their impressive rise and progressive diversification. In parallel to this
growth of FIFA’s income, it is quite natural that its expenses have been
following a similar path (see Graph 1). However, as we will see FIFA makes it
sometimes very difficult to identify precisely where the money is going. Nonetheless,
this is precisely what we wish to tackle in this post, and to do so we
will rely on the FIFA Financial reports over the last 10 years.
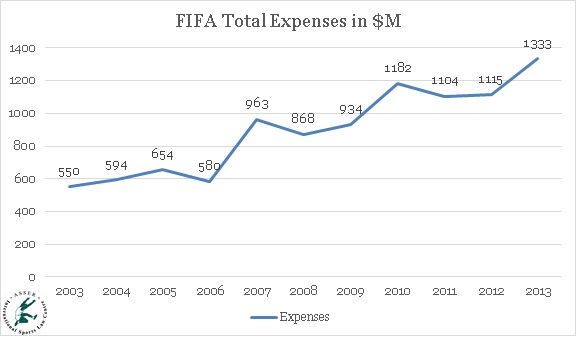
Graph 1: FIFA Expenses in USD million (adjusted for inflation),
2003-2013.
More...
On March 27, 2014, a Brazilian
court ruling authorized the
Football Players’ Union in the State of Sao Paulo[1]
to tap funds generated by TV rights agreements destined to a Brazilian Club,
Comercial Futebol Clube (hereinafter “Comercial”). The Court came to this
decision after Comercial did not comply with its obligation to pay players’ salaries. It is a peculiar
decision when taking into account the global problem of clubs overspending and
not complying with their financial obligations. Furthermore, it could create a precedent for
future cases regarding default by professional sporting clubs.
More...