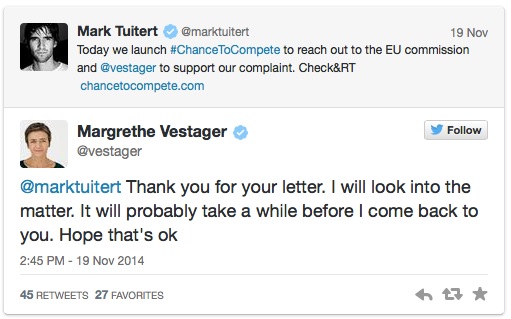
In June 2014, two prominent Dutch speed skaters, Mark Tuitert
(Olympic Champion 1500m) and Niels Kerstholt
(World Champion short track), filed a competition law complaint against the
International Skating Union (ISU) with the European Commission.
ChanceToCompeteTwitter.png (50.4KB)
Today, the
European Commission announced that it has opened a
formal antitrust investigation into International Skating Union (ISU) rules
that permanently ban skaters from competitions such as the Winter Olympics and
the ISU World and European Championships if they take part in events not organised
or promoted by the ISU. The Commissioner for Competition, Margrethe Vestager, stated that the Commission "will
investigate if such rules are being abused to enforce a monopoly over the
organisation of sporting events or otherwise restrict competition. Athletes can
only compete at the highest level for a limited number of years, so there must
be good reasons for preventing them to take part in events."
Since
the case originates from legal advice provided by the ASSER International
Sports Law Centre, we thought it would be helpful to provide some
clarifications on the background of the case and the main legal issues at
stake.
1.
What are the events leading to the complaint?
In
December 2011, a private entity, Icederby International, informed the ISU of
its intentions to start organising international speed skating events with an
innovative competition format, combining long track and short track skating. At
that time, Icerderby International was considering hosting betting activities
on the races alongside the tracks.
In
January 2012, the ISU issued a revised Code of Ethics stipulating that
persons subjected to the Code ought “to
refrain from participating in all forms of betting or support betting or
gambling related to any event/activity under the jurisdiction of the ISU”.
In
November 2013, Dubai is awarded the organisation of the World Expo 2020.
Icederby International secured a contract to organise an annual speed skating
event in Dubai as part of the programme leading up to the World Expo. The first
Dubai Icederby Grand Prix Exhibition 2014 was to take place in October 2014.
The organisers clarified that there would be no on-site betting activities
during the planned Icederby events since betting activities are strictly
prohibited in Dubai.
In
March 2014, the ISU nonetheless issued a statement (Communication No. 1853) saying that, because
the competitions organised by Icederby International are “possibly being closely connected to betting”, they would not
sanction them. The ISU also threatened that anyone participating in events
organised by Icederby International would become persona non grata within the ISU.
2.
Persona non grata … what does that mean?
According
to the ISU Eligibility rules,[1]
a person skating or officiating in an event not sanctioned by the ISU and/or
its Members (i.e. the individual national associations) becomes ineligible to
participate in ISU activities and competitions (Rule 102, para. 2 (ii)). This
sanction applies not only to the skaters, but also to coaches, trainers,
doctors, team attendants, team officials, judges, referees, volunteers, and
anyone else engaging in a relation with the ISU.
A
person who is or has been ineligible may be reinstated as an eligible person
(Rule 103, para. 1). However, this does not apply to a skater that participated
in a non-sanctioned event (Rule 103, para. 2). In other words, once a skater
participates in an event not organised or promoted by the ISU, he or she is
banned for life from participating in the Winter Olympic Games or any of the
ISU events such as the World and European Championships. In practice this would
put an end to the athlete’s sporting career.
3. Why is the ISU allegedly violating
the EU competition rules?
The
complainants contend that the ISU Eligibility Rules, in particular Rule 102, as
well as its enforcement by the ISU in the case at hand, constitutes a violation
of Articles 101 and 102 TFEU. The main premise of the complaint is that the
sanction of a lifelong ban cannot be considered inherent and proportionate to
the pursuit of any legitimate objective.
The
ISU Eligibility Rules are laid down in the ISU General Regulations, which the
Members of the ISU have adopted. This is a decision taken by an association of
associations of undertakings, within the meaning of Article 101(1) TFEU. By
their very nature, the restrictions imposed by the Eligibility Rules have the
potential to restrict competition because they raise virtually insurmountable
barriers to entry and expansion on the market for the organisation of
international speed skating events (i.e. the organisation of such events
require access to the human resources controlled by the ISU). This directly and
manifestly affects the interests of the skaters (and ultimately has the
potential to harm the welfare of sports fans).
Additionally,
the ISU and its Members enjoy a position of collective dominance, which amounts
to an absolute monopoly, on the market for the organisation of international
speed skating events.[2]
The ISU Eligibility Rules enable the ISU (and its Members) to prevent or impede
effective competition on the market for international speed skating events. In
short, the complainants argue that the ISU effectively abuses its powers to
foreclose competitors on this and other related markets. The ISU Eligibility
Rules are not simply there “on the books” but are actively invoked by the ISU
to deter skaters (and officials etc.) from breaching these rules by
participating/officiating in non-sanctioned events.[3]
The
initiative to launch the Icederby International Competitions exemplifies that
there is a demand for more international speed skating events in addition to
those that the ISU administers, both in terms of new competition formats and
competing events. This need is also evident from the limited prize money that
is available for long track and short track skaters in ISU sanctioned
international speed skating events. The prize money available for individual
skaters in a typical season with 21 international speed skating competitions
(13 long track / 8 short track) is a minimum of $ 0 and maximum of $ 109,000
(long track) / $ 31,900 (short track). If speed skaters would be able to
participate in the Dubai Icederby Grand Prix, which is but one out-of-season
single event, they would earn individually a minimum of $ 37.650 and a maximum
of $ 130,000. In other words, a short track skater could earn more by simply
participating in the Icederby event than he/she would be able to earn by
winning all of the ISU sanctioned international competitions during an entire
season.
While
the ISU’s decision not to sanction the Icederby International Competitions is
an important contextual element, the complainants are not asking the European
Commission to denounce that decision. Rather, their complaint focuses entirely
on the disproportionate sanction prescribed by Rule 102(2) of the ISU General
Regulations. Because Icederby International is the first major organisation
that wishes to organise international speed skating events without the ISU’s
approval, the radical anti-competitive nature of the ISU Eligibility Rules has
only now manifested itself. Any other (future) initiative to organise a
non-sanctioned international speed skating event would likewise face the
disproportionate restrictions imposed by the ISU Eligibility Rules.
It
is undisputed that an international sports federation, such as the ISU, may
legitimately assert the interests of the sport it administers. Yet it is
doubtful that the ISU could rely on its Code of Ethics (that only applies to
events and activities “under the jurisdiction of the ISU”) to render
ineligible any person skating or officiating in events in compliance with
national laws. Sole participation in a non-sanctioned speed skating event
should not constitute a threat to the integrity of speed skating that would
justify a total ban.
4. What is the remedial scope of EU
competition law?
The
ISU Eligibility rules and the ISU’s conduct deprive speed skaters from the
benefits that a situation of fair and open competition on the market for the
organisation of international speed skating events would offer them. The scope
for intervention on the basis of EU competition law is evident from previous
decisional practice.
In
the FIA case, the European Commission was confronted with similar
rules contained in several regulations notified by the Fédération International de l’Automobile (FIA). The International
Sporting Code of the FIA provided that no licence holder could participate in
an international Formula One event that is not entered on the FIA calendar.
Anyone that would not comply with this provision would have their licence withdrawn
and thus would be excluded from any event authorized by FIA. This and other
restrictive rules led the Commission to make, in its Statement of Objections,
the preliminary assessment that FIA “was
using its regulatory powers to block the organization of races which competed
with the events promoted or organized by FIA (i.e. events from which FIA
derived a commercial benefit”.[4]
The Commission eventually closed the case after having reached a settlement
with FIA, which provided inter alia
that FIA no longer would prevent teams and circuit owners to participate in and
organise other races provided that essential requisite safety standards are
met.[5]
More
recently, National Competition Authorities (NCAs) have also intervened on the
basis of national and EU competition law. For example:
In Sweden, the Market Court confirmed that two clauses
in the Swedish Automobile Sports Federation (SBF)’s Common rules, according to which its members were forbidden from
participating as drivers and event staff in races not sanctioned by the SBF,
violated Article 101 TFEU.[6]
The Court therefore upheld the decision of the Swedish NCA, which obliged the
SBF to amend its Common rules so that they no longer prevent licence
holders from applying for, participating in or being functionaries at
unsanctioned motor races.[7] In
2014, the Swedish NCA also closed an investigation into a loyalty clause
applied by the Swedish Bodybuilding Association (SKKF) after the SKFF committed
no longer to suspend or fine athletes, coaches, officials or judges for
participating in non-sanctioned competitions.[8]
In Italy, the NCA launched antitrust investigations
into the regulations and conduct of the national motor sports federation (ACI)
and equestrian sports federation (FISE) under Articles 101 and 102 TFEU. The
FISE investigation focused on clauses forbidding FISE members from
participating in equestrian events and activities organized by other entities
(subject to exclusion from the federation). The investigation was closed after
FISE committed to remove the anti-competitive clauses from its statutes. FISE
also committed to allow the use of its affiliated clubs’ facilities by
independent event organizers.[9]
The ACI investigation focused on several regulatory and statutory provisions
intended to limit access to the market for the organization of motor sport
events for competitors. In 2009, the NCA adopted a commitment decision after
the ACI undertook to inter alia allow
its members to participate in events not organized by the federation.[10]
In Ireland, the NCA opened an investigation into a
rule of Show Jumping Ireland (SJI) that prevented members of the SJI to compete
at unaffiliated show jumping events. The case was closed after the SJI
committed to amend the rule to address the competition concerns. Since then,
members of SJI who enter into unaffiliated show can only be penalized if the
show has not signed up to the specified Health and Safety Standards and has not
provided the SJI with evidence of adequate insurance.[11]
Two
important lessons can be drawn from this decisional practice.
First,
save for compliance with objective technical safety standards, the decisional
practice has consistently found that rules prohibiting the participation of its
members in non-sanctioned events violated Articles 101 and/or 102 TFEU and had
to be abolished. Evidently, to be deemed proportional, the sports federation would
still be required to prove that a certain non-sanctioned event would be less
safe than its own events.[12]
Second,
all national cases dealt with rules of national federations. In the Swedish
bodybuilding case (2014), the contested rule was the national equivalent of a
clause contained in the Constitution of the International Bodybuilding
Federation. Yet the remedial action was purely national in scope.
The SKKF committed no longer to apply the restriction in Sweden, but the rule
continues to be enforced by the IFBB and all other European member federations.
The much wider scope of the parties affected by a rule from an international
sports federation makes it necessary to tackle the restriction at the EU level.
5. What are the next procedural steps?
Since
this is the first time in more than a decade that the European Commission is
conducting an in-depth antitrust investigation in the field of (regulatory
aspects of) sport, the decision to open proceedings delivers a powerful
message.
The
opening of an in-depth antitrust investigation does not prejudice the finding
of a violation of the European competition rules, however. It only signals that
(1) the initial assessment led to the conclusion that there are “reasonable
indications of a likely infringement” and (2) the Commission will further
pursue the case as a matter of priority with a view to adopting a decision.[13]
The Commission will thus allocate recourses on the case and endeavour to resolve
the case in a timely manner.
Unless
the Commission would in the end conclude that there is not sufficient evidence
to find an infringement, the case will be resolved through the adoption of a
prohibition or commitment decision.
The
ISU could offer commitments suitable to address the competition concerns
arising from the investigation. The Commission might then conclude that there
are no longer grounds for actions. Instead of formally establishing a violation
of the EU competition rules, a commitment decision will simply make those
commitments legally binding. In the alternative, the Commission will proceed to
a prohibition decision, requiring the ISU to bring the infringements to an end.
For this purpose, it may impose on the ISU remedies proportionate to the
infringement committed and necessary to bring the infringement to an end and
impose a fine.
6. Why is this case so important?
Needless
to say, the stakes are significant and extend well beyond the sport of speed
skating.
Only
a handful of international sport federations have truly experienced the “Bosman
effect” and faced scrutiny of their regulatory overreach under the European
competition rules. The fact that most international sports federations are
based in Switzerland, outside the EU, may further explain a lack of awareness
about the need to comply with EU competition law. Of course, this does not mean
they are immune: anti-competitive practices that appreciably affect the EU
market are drawn into the net of EU competition law.
While
the compliance of sporting rules with EU competition law needs to be assessed
on a case-by-case basis, the European Commission did present an indicative list
of sporting rules that are likely to infringe Articles 101 and 102 TFEU in its 2007 White Paper on Sport. Rules shielding
sports associations from competition are mentioned. Other than in the area of
revenue generating activities related to sport (in particular the sale of
sports media rights), however, the body of competition case law at the EU level
dealing with organisational sporting rules is limited. Even though sports
associations usually have practical monopolies in a given sport, the remedial
potential of EU competition law to influence their regulatory actions (that
often have significant economic consequences) remains underexplored.[14]
The
Commission’s decision to pursue this case therefore has an important
precedent-setting value. This is particularly true for the numerous
international sports federations that also disproportionally restrict athlete
participation in unsanctioned events with penalties ranging from fines, periods
of ineligibility, and lifetime bans. For instance:
International
Federation of Volleyball (FIVB): since 2009, all athletes that take part in
unauthorized beach volleyball events will have their membership withdrawn for
all FIVB competitions (period of ineligibility up to a life ban).[15]
Surprisingly, different sanctions apply to participation in volleyball
competitions of non-FIVB recognized organizations (e.g. a fine on the club
involved of CHF 30.000 and suspension of the club, teams, players, and
officials involved for a period up to two years).[16]
International
Swimming Federation (FINA): any affiliated member having any kind of
relationship with non-affiliated bodies shall be suspended for a minimum period
of one year up to a maximum period of two years.[17]
International
Netball Federation (INF): any person participating in any capacity in an
unsanctioned event is automatically ineligible to participate in INF events for
a minimum of 12 months thereafter.[18]
International
Gymnastics Federation (FIG): gymnasts taking part in unsanctioned competitions
or exhibitions may not claim to be eligible to participate in the Olympic
Games.[19]
International
Cricket Council (ICC): other than in exceptional circumstances, a person
participating in unofficial cricket events shall not be selected or permitted
to participate in official events for a minimum of one year thereafter.[20]
International
Hockey Federation (FIH): any athlete or other individual participating in an
unsanctioned event is automatically ineligible for one year to participate in
any FIH event.[21]
The
mere threat of drastic sanctions, combined with the general lack of objective,
transparent, and non-discriminatory rules governing the authorization of
international sports events, enables federations to de facto block events that could compete with the events they
organise and promote. In the absence of sufficient procedural safeguards, this clearly
raises concerns about a conflict of interest between a federation’s power to
authorise the organisation of events and the federation’s commercial interests
in promoting its own events.
The
ISU case will hopefully provide a much-needed reminder to sports federations
that without valid justifications they cannot use their private regulatory
power to foreclose competitors or hinder the freedom of EU athletes and sports
personnel to exercise economic activities.
Disclaimer: the author represents and
advises the complainants in their antitrust proceedings.
[1] ISU General
Regulations (2014), available at http://static.isu.org/media/165642/constitution-and-general-regulations-version-july-31-2014.pdf
[2] This has already been recognized by the German courts in the Pechstein
case.
[3] In its 2014 statement (Communication No. 1853), the ISU found it opportune to remind all its members “that
participation in any international ice skating competition not sanctioned by
the ISU will result in the loss of eligibility of the participants”.
[4] Notice published pursuant to Article 19(3) of Council
Regulation No 17 concerning Cases COMP/35.163, Notification of FIA Regulations,
COMP/36.638, Notification by FIA/FOA of agreements relating to the FIA Formula
One World Championship, COMP/36.776
GTR/FIA & others (2001/C 169/03), OJ C169/6-7
[5] European Commission, XXXIst Report on Competition
Policy 2001, para. 221 et seq.
[6] Swedish Market Court's ruling
2012:16 in Case A 5/11, Svenska
Bilsportförbundet v Konkurrensverket (December 20, 2012) available at http://www.kkv.se/t/NewsArchive.aspx?id=529 (see also e.g. http://www.kkv.se/t/NewsPage____8672.aspx ).
[7] Konkurrensverket (Swedish Competition Authority)
Decision of 13 May 2011 in Case 709/2009, available at http://www.kkv.se/upload/Filer/Konkurrens/2011/Beslut/09-0709.pdf.
[8] Konkurrensverket (Swedisch Competition Authority)
Decision of 28 May 2014 in Case 590/2013, available at http://www.konkurrensverket.se/upload/Filer/Konkurrens/2014/13-0590.pdf.
[9] Autorità Garante della Concorrenza e del Mercato, Federitalia/Federazione Italiana Sport Equestri (FISE), Decision
n°18285 of 28 July 2008, Bolletino n° 19/2008.
[10] Autorità Garante della Concorrenza e del Mercato, Gargano Corse/ACI, Decision n° 19946 of 30 June 2009, Bolletino n°
23/2009.
[11] The Competition Authority, Show Jumping Ireland, case summary available
at http://www.tca.ie/images/uploaded/documents/201205%20Case%20Summary%20-%20SJI.pdf
[12] Swedish Market Court's ruling 2012:16 in Case A 5/11, Svenska Bilsportförbundet v Konkurrensverket
(December 20, 2012) available at http://www.kkv.se/t/NewsArchive.aspx?id=529; The Competition Authority, Show Jumping Ireland, case summary
available at http://www.tca.ie/images/uploaded/documents/201205%20Case%20Summary%20-%20SJI.pdf.
[13] European Commission, Antitrust Manual of Procedures (2012), available
at http://ec.europa.eu/competition/antitrust/antitrust_manproc_3_2012_en.pdf
[14] Ben Van Rompuy, "The role of EU competition law in tackling abuse
of regulatory power by sports associations" (2015) 22 Maastricht Journal
of European and Comparative Law 2, 174-204.
[15] FIVB, Beach Volleyball Handbook 2013, Article 9.1 and 11.3.
[16] FIVB, Disciplinary Regulations, Article 15.2 and Sports Regulations
Volleyball, Article 46.6.
[17] FINA, General Rules 2013-2017, Rule GR4.
[18] INF, General Regulations – Appendix – Regulations on Sanctioned &
Unsanctioned Events: Guidance Notes (August 2013).
[19] FIG, Technical Regulations, Appendix B (Rules of Eligibility for the
International Gymnastics Federation).
[20] ICC, Regulations for Approved/Disapproved Cricket and Domestic Cricket
Events, Section 32.4.
[21] FIH, Regulations on Sanctioned & Unsanctioned events, Article 2.