Editor's note: Branislav
Hock (@bran_hock) is PhD Researcher at the Tilburg Law and Economics Center at Tilburg
University. His areas of interests are transnational regulation of corruption, public
procurement, extraterritoriality, compliance, law and economics, and private
ordering. Author can be contacted via email: b.hock@uvt.nl.
This blog post is based on a paper
co-authored with Suren Gomtsian, Annemarie Balvert, and Oguz Kirman.
Game-changers that lead to financial
success, political revolutions, or innovation, do not come “out of the blue”;
they come from a logical sequence of events supported by well-functioning
institutions. Many of these game changers originate from transnational private
actors—such as business and sport associations—that produce positive spillover
effects on the economy. In a recent paper forthcoming
in the Yale Journal of International Law, using the example of FIFA, football’s
world-governing body, with co-authors Suren Gomtsian, Annemarie Balvert, and
Oguz Kirman, we show that the success of private associations in creating and
maintaining private legal order depends on the ability to offer better
institutions than their public alternatives do. While financial scandals and
other global problems that relate to the functioning of these private member
associations may call for public interventions, such interventions, in most
cases, should aim to improve private orders rather than replace them.
FIFA example – from gentlemen’s agreements to a rich global
regulator
FIFA is the
governing body for football (or soccer, as it is known in some countries). Founded
in 1904 under Swiss law by seven football associations, just 40 years ago, FIFA
was a small gentlemen's club with a staff of 11, far from politics, which
produced little cash. Since then, it has evolved into a powerful organization
generating billions of dollars in annual revenues through sales of media and
marketing rights; now it employs hundreds. The rise of FIFA has been a
continuous process that was made possible by the reluctance of states and
supra-national organizations such as the European Union (EU) to intervene in
the governance of sport, particularly football. Hence, supported by and
benefitting from the special treatment of sports, FIFA filled the regulatory
gap and strengthened its status as a private regulator.
Besides the rules of the game, FIFA’s
legal order includes privately-designed rules of cooperation and a complex
organizational structure that spans every involved party including players,
clubs, coaches, managers, club investors, officials, sponsors, and spectators. The
centerpiece of the relations regulated by the rules of FIFA are
employment-related questions. Most
importantly, FIFA’s Transfer Regulations create strong tensions between FIFA’s regulatory autonomy
and public orders such as the sovereign jurisdictions of FIFA’s member
associations and supra-national organizations. Tensions between
different levels of employment rules are especially visible in matters related
to equality and/or non-discrimination of workers, the treatment and
qualification of minors, the freedom to choose employment, and the freedom of
movement. For example, the inability of players to terminate their contracts
without cause, before expiry and without paying compensation, is in stark
contrast with traditional employment laws, according to which employees are
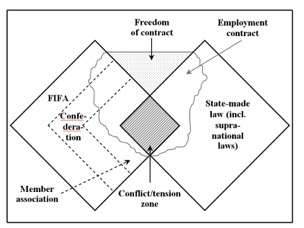
free to end employment without cause by prior notice. Figure below illustrates
the relationships between the different levels of “football ordering” and
public ordering when it comes to labor rules.
The Relationship of
Labor Rules in Football
Furthermore, FIFA has also private dispute
resolution venues and sophisticated system of sanctions and incentives
promoting compliance with the decisions of the private order’s dispute resolution
bodies. Possible sanctions vary but they are leveraged by the
monopoly power of FIFA. Consider the right of FIFA to suspend a member
association for a specific period or expel it fully from FIFA for failure to
comply with its obligations, including an obligation to comply with FIFA or CAS
decisions. Given FIFA's monopoly, this, in fact, means that national teams and
licensed clubs from the suspended or expelled country cannot participate in any
organized game. As a consequence,
FIFA has been able to maintain cooperation among all involved actors, yet,
along with the increasing commercial dimension, the incentives of states and
other public orders, particularly the EU, to intervene have grown.
Integrity vs. legal order
The fact that FIFA is undermined by
corruption is nothing surprising. Prof. Alina Mungiu-Pippidi shows that
the average public integrity in more than 200 countries whose soccer
associations are the FIFA constituents “is just 5, on a scale where New Zealand
has ten and Somalia 1” […] “Were FIFA a country, it would clearly not be in the
upper half, but somewhere near Brazil, whose officials seem to have been waist
deep in its corruption, and which ranks around 121, with a 4.2”. FIFA’s administrative structure, certainly,
needs reforms that will improve its financial stability and decrease corruption
risks within the organization. These reforms, indeed, may require “public
nudge” by the enforcement of extraterritorial “anti-mafia” statutes such as the
US Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organization Act (RICO)
that played the central role in the so-called FIFAGate.
Moreover, in the light of “the second FIFAGate”—six months after the original scandal, a number of FIFA
officials that replaced the old leadership were charged with a 92-count
indictment—and after the recent neutralization of its internal corruption
investigations (see here),
more radical “public nudge” may be desirable. Indeed, these developments, as
was discussed in this blog
some time ago, may call for a more powerful intervention by, for example, the
EU, to impose ‘certain basic “constitutional” requirements’ to FIFA.
Nevertheless, while FIFA may need
“public help” to clean its house and improve some areas of its legal order, no
public order is a better alternative. Common rules spanning across borders,
predictable contractual relations, and incentives to invest in training young
players are only some advantages made possible by FIFA’s tailored rules of
behavior. These advantages would be lost if public interventions would crash
the FIFA order and replace it by a patchwork of national laws, unstable
contractual relations, more costly dispute resolution and enforcement
mechanisms, and limited ability to encourage talent development. Therefore,
while FIFA as an administrative organization may generally be considered as more
corrupt than an average government, it has been able to offer harmonized
institutions that in many cases are better accustomed to the needs
of the involved parties than their state-made alternatives, which often are
based on one-size-fits-all approach and lack certainty of application.
Public orders as the reversed civil
society
It does not mean that public orders
such as the EU and nation states should do nothing. Private entities often need
a “public nudge” not only to prevent excesses, but also to maintain incentives
to produce rules that reflect new economic and social developments. In numerous
writings (for an overview see Katz),
law-and economics scholars indicate that while in principle private orders
should be best left alone, states should limit the potential of powerful
interest groups to undermine the roots of private orders such as FIFA. Who, how,
and when should determine the benchmark of what is excessive is difficult, and law-and
economics has declined to offer a general theory of the role of public orders
in nudging private orders to limit interest groups’ power. Nevertheless, determining
the role of public orders is no more difficult than the question what civil
society should do when it comes to the performance of nation states.
In the context of nation states, the
key role in limiting the power of elites belongs to the civil society. In case
of monopolistic orders such as FIFA’s, however, there is often no direct
representation of various actors inside such orders. Shouldn’t, then, states and
the EU assume the role of a reversed civil society when interacting with large
and successful private orders? In practice, particularly the EU is more and
more involved in an informal co-determination of football-related regulation
(for similar argument see here).
For example, the recent social dialogue in European football, brokered
by the EU Commission, is an example how public orders can fulfill their role as
reversed civil society. The EU Commission, instead of intervening directly and
regulating sports, encouraged, and should do so much more, various stakeholder
groups, such as the European Club Association and FIFPro, to engage in a
dialogue with the purpose of improving the practices of player protection
(however, it is true that the EU Commission had a way deeper impact through EU
competition law, see Duval).
For the private order itself participation in this dialogue and active
encouragement of the enforcement of its results is the best way to guarantee its
role as a supplier of rules (see generally Colucci &
Geeraert). In contrary, refusal to accommodate certain mechanisms,
and mainly these that effectively limit FIFA’s executives’ power (e.g. Ethics
Committee), may lead to a forceful, but legitimate, public intervention with
possibly tragic consequences for the world of football.
Conclusion: Taking over fallen
FIFA
What is so fascinating about FIFA is that it
exemplifies how a very small number of enthusiastic people could set a
mechanism that is ultimately able to create institutions that aim to regulate
behavior of involved actors globally as well as to keep them away from regular
courts. FIFA is an example of an order that has created huge economic and
social value by being able to overcome many hurdles that prevented countless
other member associations from creating their own orders (think of lawyers or
investment bankers, for example). The fact that such order locks-in all
involved football actors, despite some, such as small teams, benefiting
significantly less by their participation than others, suggests that there is a
value, despite FIFA’s monopoly power, that alternatives cannot offer. Some of them, such as
increased certainty, are in the interests of all involved actors, whereas
others, such as commitment to enforce contractual practices or training
compensation awards, are more preferred by sophisticated actors (i.e. clubs and
prominent footballers) and small clubs, respectively. This, though not allowing
to state plainly that the private order is maximizing the welfare of all
involved actors, also does not justify arguments for abandoning the current
system in favor of state laws. In contrary, failure to accommodate mechanisms
that limit the power of inside interest groups might undermine the order by
giving incentives to interest groups to advocate public orders’ involvement,
thereby putting an end to the monopoly of FIFA’s order, and possibly its destruction.