Update: On 14 April footballleaks released a series of documents concerning Sporting de Gijón. Therefore, I have updated this blog on 19 April to take into account the new information provided.
Doyen Sports’ TPO (or TPI) model has been touted as a “viable alternative source of finance much needed by the large majority
of football clubs in Europe". These are the
words of Doyen’s CEO, Nélio Lucas, during a debate on (the prohibition of) TPO
held at the European Parliament in Brussels last January. During that same
debate, La Liga’s president, Javier
Tebas, contended that professional football clubs, as private undertakings,
should have the right to obtain funding by private investors to, among other
reasons, “pay off the club’s debts or to compete better”. Indeed, defendants
of the TPO model continuously argue that third party investors, such as Doyen, only
have the clubs’ best interests in mind, being the only ones capable and willing
to prevent professional football clubs from going bankrupt. This claim constitutes
an important argument for the defendants of the TPO model, such as La Liga and La Liga Portuguesa, who have jointly submitted a complaint in front of the
European Commission against FIFA’s ban of the practice.[1]
The eruption of footballleaks provided the essential material necessary to test this claim. It allows
us to better analyse and understand the functioning of third party investment and
the consequences for clubs who use these services. The leaked contracts between
Doyen and, for example, FC Twente, showed that the club’s short term financial
boost came at the expense of its long-term financial stability. If a club is
incapable of transferring players for at least the minimum price set in Doyen’s
contracts, it will find itself in a financially more precarious situation than
before signing the Economic Rights Participation Agreement (ERPA). TPO might
have made FC Twente more competitive in the short run, in the long run it
pushed the club (very) close to bankruptcy.
More than four months after its launch, footballleaks continues to publish documents from the football
world, most notably Doyen’s ERPAs involving Spanish clubs. For this blog, our
dataset will cover the two ERPAs between Doyen and Sporting de Gijón (found here and here); the ERPAs between Doyen and Sevilla FC for
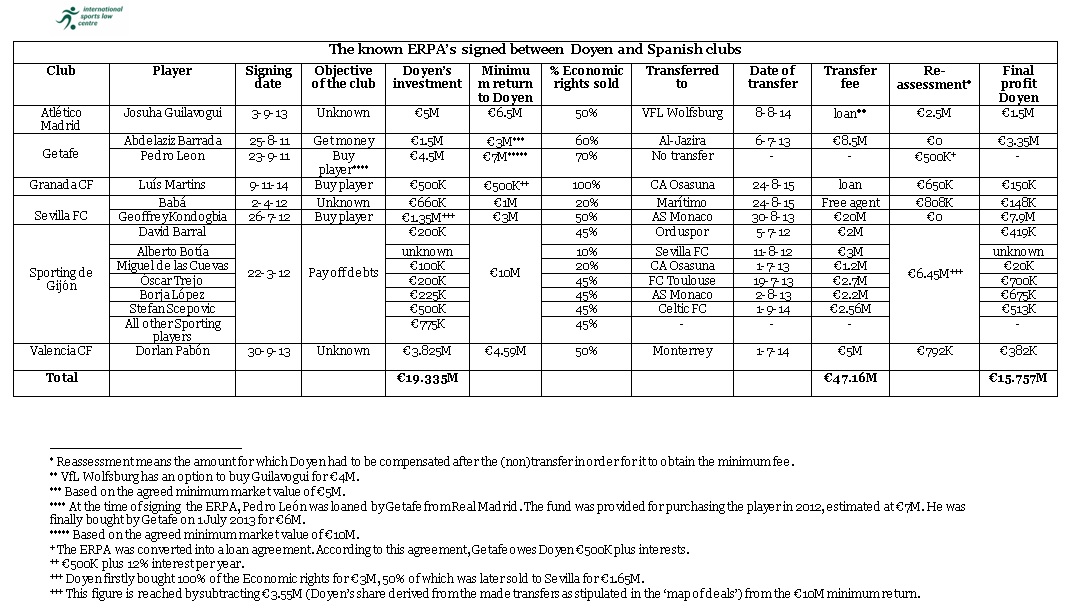
Kondogbia and Babá; the ERPAs between Doyen and Getafe for Abdelazziz Barreda and Pedro León; the ERPA between Doyen and Granada CF for Luís Martins; the ERPA between Doyen and Atlético Madrid for Josuha Guilavogui; and the ERPA between Doyen and Valencia CF for Dorlan Pabón.
The first part of this blog will provide background information on the
recent economic history of Spanish football. The posterior in-depth analysis of
the ERPAs will thus be placed in context. The blog will also include a table
with the relevant facts from the ERPAs completed with the information included
in an Excel document showing a map of deals and transactions allegedly conducted by Doyen and recently published on footballleaks. Relevant facts and
figures that are not found in the ERPAs or in the Excel document, will be taken
from the website www.transfermarkt.de. Based on the
outcome of the analysis, we will attempt to conclude whether, and to what
extent, the ERPAs have been profitable for the clubs involved, from a financial
and competitive perspective.
Financial misery and TV
rights inequality off the field
The financial misery
Spain was one of the countries most affected by the global financial
crisis that commenced in 2008. The unemployment rate was above 25% for a long period of time and its budget deficit was
about 10% from 2008 to 2012. The (professional) football sector also suffered
from this general financial crisis. A study on the financial situation of Spanish clubs during the period 2007-2011 shows that by June 2011, 80% of La Liga clubs had a negative working
capital. This meant that the clubs’ short term assets were not enough to cover
the short term debts. The study further explains that the main reason for the
financial difficulties is the excess of expenditures on players, i.e. paying
transfer fees and salaries that clubs cannot afford. Not surprisingly, by 2011,
half of the clubs from the Spanish first and second division had entered bankruptcy proceedings. A large part of the total debt was owed to the Spanish public
authorities. In 2012, clubs in Spain's top two divisions collectively owed some
€750 million to the tax authorities and another €600 million to the social security system. One of the
teams who signed ERPAs with Doyen, Atlético Madrid, was known to have a tax
debt which accounted for a fifth of the entire league’s tax debt. In fact, their tax debt of over €120 million amounted to over 60% of
their annual revenue. Almost 40% of the clubs in the top two divisions
presented negative equity, meaning that they were in clear need for funds from
other parties. The general economic crisis prevented clubs to get these funds
through normal means, like shareholders, members, sponsorships and bank loans. Local
authorities were many times willing to aid their clubs. For example, the
municipality of Gijón had rescued Sporting de Gijón by relocating its youth training
facilities and subsequently buying the facilities for
€12 million. Another example is that of Valencia CF. In its ambition to
grow, the club decided to build a new stadium. The idea was to finance the new
stadium by selling the old stadium. Once again, due to the financial crisis,
and particularly the collapse of the housing market, it suddenly was incapable
of selling the old stadium for the required price. The construction on the new
stadium had already commenced with loaned money which could not be paid back. The
municipality’s decision to place a State guarantee on this loan has been the
subject of a formal State aid investigation by the European Commission.
TV Rights income inequality
One of the most important ways to generate income for professional
football clubs is through the selling of TV rights. The Spanish clubs combined generated
roughly €700 million per year from the selling of TV rights between 2010 and 2015.[2]
This is slightly more than the €628 million the German Bundesliga was making per year
between 2013 and 2016, but less than €940 million the Italian league was making in the
2012-13 season. The English Premier League is in a league of its own in this regard, which is making about €1.2
billion per year from the 2013-14 season onwards.[3]
Notwithstanding the total €700 million a year, most Spanish clubs do not
derive enough money from selling the TV rights to compensate their losses. One
has to keep in mind that where the clubs of Europe’s other major football
leagues (e.g. England, Germany, France and Italy) were selling their TV rights
jointly, Spanish clubs were still selling their TV rights individually. By
means of the individual selling system, Spain’s two most popular clubs, Real
Madrid and FC Barcelona, were capable of selling their TV rights for much more
money than the other clubs. In the 2010/11 season for example, out of
the €641 million generated in total, FC Barcelona got €163 million, whereas
Real Madrid got €156 million. The remaining 16 clubs of La Liga had to share the remaining €322 million, which is slightly
more than €20 million per club on average. By contrast, the ‘smaller clubs’ of
the English Premier League were still making at least €49 million in that same season,
which is two-and-a-half times as much as their Spanish counterparts.[4]
Even the club that was earning least money in Italy in 2012, Pescara, was
earning more per year from the selling of TV rights than the average Spanish
club (€25 million).
Calls for a fairer distribution of TV rights income in Spain have been
heard for years, particularly from the smaller clubs, but the switch to a joint selling system will only take place as of the start of the 2016-17 season. It is
believed that continuous lobbying by Real Madrid and FC Barcelona against the joint selling system is the main reason for this delay. In
a way, it could be argued that apart from reckless risks on the transfer market
and the effects of the Spanish financial crisis, the dominant position of Real
Madrid and FC Barcelona is what led to many Spanish clubs being in severe financial
difficulties. The urge of these clubs to turn to investment companies like
Doyen becomes more understandable, given that the system itself did not allow
them from obtaining funds from other ‘normal’ sources.
The ERPA’s and its
aftermaths explained
On the day of writing this blog (12 April 2016), nine ERPAs between
Doyen and Spanish football clubs were published on the website of footballleaks. The ERPAs are divided in
two groups: Firstly, the ERPAs that proved to be successful for both the club
and Doyen are analysed; the second part combines all the ERPAs in which the
players concerned were either not sold for high enough profit, or not transferred
at all. As will be shown, these ERPAs had mostly negative financial
consequences for the clubs.
The successful ERPAS:
Kondogbia and Barrada
Sevilla’s recent sporting successes, most notably
winning the Europa League four times since 2006, are said to have been the
result of a high level youth academy combined with an excellent scouting
network. However, it has never been a secret that Sevilla made use of the
services provided by Doyen, including the signing of ERPAs. In a well-publicised seminar on TPO that took place in April 2015, Sevilla defended the TPO model and made
clear that it was against an outright ban of the practice. The ERPA concerning Geoffrey Kondogbia and his subsequent transfer to AS Monaco can explain why Sevilla is in
favour of the TPO model. Kondogbia was transferred from RC Lens to Sevilla on
the same date as the signing of the ERPA (26 July 2012) for €3 million. With
the objective of obtaining 100% of the Economic rights, Doyen paid RC Lens the
full amount of the transfer fee. In turn, Sevilla would buy from Doyen 50% of
the economic rights for €1.65 million. Even though the minimum transfer fee was
set by the parties at €6 million, Kondogbia was sold only one year later to AS
Monaco for a staggering €20 million. An excellent deal for Doyen, which registered
a profit of €7.89 million.[5]
This ERPA is an example of a collaboration between a club and an investment
fund, which has been highly profitable for both. With the “help” of Doyen,
Sevilla managed to sign a young player and sell him for a profit not long
after. However, as can be seen below, even Sevilla has signed ERPAs that have
not been very beneficial for the club.
A second “successful ERPA” signed between Doyen and a Spanish club was the ERPA between Doyen and Getafe for Barrada. Similar to many other ERPAs, it stipulated that Getafe was not able to
obtain financial support from the banking system due “to the current financial
crisis”. Therefore, Getafe decided to sell 60% of the economic rights of one of
its most promising young players for €1.5 million to Doyen. Both parties agreed
that the minimum transfer value of Barrada was €5 million. Consequently, as can
be deducted under paragraph 7 of the ERPA, Doyen’s minimum return would always
be at least €3 million (60% of €5 million), guaranteeing Doyen a profit of €1.5
million (€3 million minimum return minus €1.5 million grant fee). The minimum
return was easily surpassed after Barrada was transferred to Al-Jazira for €8.5
million in 2013. In accordance with Doyen’s own figures, the investment fund
obtained €3.35 million for this transfer, a profit of 223%.[6]
The many “failed”
ERPAs
Atlético Madrid was no novice to the practice of TPO when it sold 50% of
Joshua Guivalogui’s economic rights for
€5 million to Doyen. As can be seen from the ‘Map of Deals’, Atlético had
previously sold 33% of the economic rights of the highly successful Atlético
player, Falcao, to Doyen for €10 million. His later transfer to AS Monaco for
€43 million was probably also economically beneficial for Atlético. Guivalogui,
however, has been less successful wearing an Atlético shirt. He has played
seven games in total for the club in two-and-a-half years, having been loaned
to St-Étienne for the 2013-14 season, and to VfL Wolfsburg for the 2014-15 and
2015-16 seasons. If Wolfsburg decides to lift the option it has to buy Guivalogui
for €4 million[7],
Atlético Madrid will probably need to pay an additional amount to Doyen in
order to reach the agreed minimum fee of €6.5 million.[8]
As regards Sevilla FC, where the ERPA concerning Kondogbia can be seen
as “successful”, Babá’s ERPA tells a completely
different story. Sevilla sold 20% of Babá’s economic rights for €660.000 to
Doyen in 2012. Nonetheless, Babá never managed to secure a spot in the Sevilla
squad and he was loaned out to Getafe and Levante between 2013 and 2015. After
his contract expired with Sevilla in the summer of 2015, he moved back to his
former club Marítimo as a free agent. Although Sevilla did not receive a fee
for this transfer, Doyen still obtained a guaranteed profit of €148.000, as can
be seen from the ‘map of deals’.
The Guivalogui ERPA and the Babá ERPA tell a similar story. Both players
did not fulfil the expectations the clubs had of them at the moment Doyen
bought parts of their economic rights. As a result, they were transferred, or
are going to be transferred, for an amount well below the agreed minimum
return. A similar run of events occurred with Luís Martins and Dorlan Pabon. Both players were
not successful at Granada and Valencia respectively, and were transferred at a
loss for the club. The exact figures of the transfers can be found in the table
below.
The ERPA’s signed between Doyen and Sporting de Gijón are particularly
interesting in terms of “failure”, because they illustrate perfectly the
desperate situation the club found itself in. Sporting has been on the verge of
disappearing not once, but several times in the last 10 to 15 years. In 2005,
its total debt amounted to €51 million, with more than half owed to the public authorities. As a result, the club entered bankruptcy proceedings. In 2007, a settlement was reached between
the club and its creditors. Even though the club still had a debt of €35.8
million, a Spanish court decided to terminate the bankruptcy proceedings. By
the second half of 2011, the club presented a positive balance
sheet at the shareholders’ general assembly for
a fifth year in a row, but in reality Sporting was still acute financial
difficulties, as the club would admit later on. It is this acute need
for money that made the club turned to Doyen twice in less than a year. The
fact that Sporting de Gijón is still alive today (albeit in danger of
relegating to the second division), makes one wonder whether the ERPA with
Doyen actually aided the club in its fight for survival or whether it worsened
the situation in a similar way as FC Twente’s.
The first agreement concerns the purchase
for €2 million of part of the economic rights of nine players who, at the time
of signing, were registered as Sporting players.[9]
Future transfers of one or more of these players would need to generate a
profit of €7 million for Doyen.[10]
The lifespan of the first agreement was not very long, as it was replaced by a second ERPA on 22 March 2012.
Indeed, Sporting de Gijón stated officially on 23 February 2016
that the first ERPA never deployed any legal effects.
The first ERPA and the second ERPA between Doyen and Sporting show some
clear similarities. For an amount of €2 million, Doyen buys 25% of the economic
rights of all the players of both the first team and Sporting B (the second
team).[11]
This percentage remains 25% until Doyen obtains an amount of €7 million
from the transfers of Sporting players to other clubs. Once this amount is
reached, the percentage will be reduced to 15% until a further €3 million is
earned by Doyen. Therefore, the minimum return Doyen should get is that of €10
million. Should Doyen not have received €7 million or more by 31 January 2015,
the percentage of the economic rights owned by Doyen of all the Sporting and
Sporting B players will be increased to 35%. Doyen's share of the economic rights would also increase to 35% if the club relegates from the first division (clause 2.5). A further important element of the ERPA is clause 4.1, by which Sporting names Doyen as the exclusive agent (intermediary) of the club for all transfer and loan operations of Sporting players.
By using the ‘map of deals’ and transfermarkt,
we have listed all Sporting and Sporting B players sold after March 2012.
These players were:
-
Davud Barral – sold
for €2 million to Orduspor on 5 July 2012;
-
Alberto Botía – sold
for €3 million to Sevilla FC on 11 August 2012;
-
Miguel de las Cuevas
– sold for €1.2 million to CA Osasuna on 1 July 2013;
-
Óscar Guido Trejo –
sold for €2.7 million to FC Toulouse on 19 July 2013;
-
Borja López - sold
for €2.2 million to AS Monaco on 2 August 2013;
-
Stefan Scepovic - sold
for €2.56 million to Celtic FC on 1 September 2014.
A closer look at the ‘map of deals’ shows one important discrepancy
compared to the ERPA of 22 March 2012. The share of economic rights owned by
Doyen were not 25% (as stipulated in the ERPA), but 45%.
Thanks to footballleaks' release of the so-called 'Escritura de Liquidación' on 14 April we now know what caused this increase. Firstly, in accordance with clause 2.5 of the ERPA, the economic rights owned by Doyen of all the Sporting players (except Botía and De las Cuevas) increased to 35%, since Sporting relegated to the second division in May 2012. Secondly, being an intermediary in all of these transfers, Doyen was entitled to an additional 10% of all the income generated from the transfers.[12] The ‘map of deals’ shows that the transfers of
Sporting players has so far led to Doyen receiving more than €3.5 million, a
profit of about €1.5 million for their €2 million investment. Nonetheless, this
figure is still well short of the minimum return Doyen expects to get of €10
million. In other words, should the ERPA still be in force, Sporting is still
required to sell more players if it is to meet its obligations towards Doyen.
Table summarizing the
analysed ERPA’s signed between Doyen and Spanish clubs
Conclusion
The reason that many Spanish clubs decided to sell economic rights of
players to companies like Doyen from about 2011 to 2015 (the year FIFA banned
the practice) is relatively straightforward: The financial crisis was heavily
felt in Spanish football, with many clubs incapable of paying off high debts
owed to the public authorities. Moreover, the difference between the financial
and competitive power of Real Madrid and FC Barcelona on the one hand, and all
the other clubs on the other was only getting bigger. Not only did competing at
national level become close to impossible, even smaller clubs from England were
generating more than twice the revenues of Spanish clubs. The chances of being
successful at European level were at risk.
Doyen was basically at the right place, at the right time. The ‘small’
Spanish clubs were in desperate need for money, either to compete or simply to
survive, and Doyen was willing to give them this money in return for (part of)
the economic rights of their football players. From the outside, it looks like
a perfect match between club and investment fund. However, was TPO profitable
for Spanish football clubs from a competitive and financial perspective?
From a financial perspective, the business is clearly lucrative for
Doyen. As can be seen in the table, by investing €19.335 million it so far made
a profit of €15.757 million.[13]
In other words, an 81.5% profit! The same cannot be said for the clubs. Only the
transfers of Barrada from Getafe to Al-Jazira and Kondogbia from Sevilla to AS
Monaco were profitable. For all the other ERPAs, it appears that an a posteriori compensation to Doyen was necessary,
because the amount obtained through the transfer could not cover the minimum
return secured to Doyen in the ERPAs.
The legal discussions on TPO to a large extent focused on whether the
practice leads to an unauthorized influence of third parties on the internal
governance and policies of a club; and on whether a complete ban is contrary to
(EU) competition law. Yet, the aspect that remains underexposed in the author’s
opinion is the severe negative financial effect TPO can have on a football
club. As we have discussed a couple of months ago in a blog on FC Twente, the financial
position of the Dutch club deteriorated after signing the ERPA to such an
extent that the club is now in serious danger of disappearing all together.
It is possible, though unlikely, that FC Twente’s downfall was an
exception. However, one should not
underestimate Sporting de Gijon’s current financial situation, for example. A
closer look at the ‘map of deals’ tells us that in March 2015 Sporting had only
paid €250.000 of the €3.5 million it owed Doyen. A total debt of at least €3
million was confirmed in an official joined statement, dated 29 February 2016. The statement further holds that this debt has
to be repaid before 2019, but one cannot help thinking that, for a club like
Sporting de Gijón, this is easier said than done. Getting the money from future
transfers should be complicated if Sporting only partially owns the economic
rights of its own players, plus a looming relegation to the second division at
the end of this season will not be beneficial either.[14]
[1] More information on the TPO ban can be
found in our previous Blogs, such as “Blog
Symposium: FIFA’s TPO ban and its compatibility with EU competition law –
Introduction”.
[2] The total amount
generated for the 2010/11 season was €641, see Mail Online, “Barca and Real consider sharing TV rights to make La
Liga more competitive”; The total amount generated for the 2014/15 season
was €742.5 million, see Marca, “Así
será el reparto del dinero televisivo”.
[3] As of the 2016-17
season, The English Premier League will make €2.1 billion per year, see Mail Online, "Premier League set for £3bn windfall from global TV rights as rival broadcasters slug it out to screen England-based superstars"
[4] More information on
the selling of TV rights in football can be found in our previous Blogs, such as “Why the European Commission will not
star in the Spanish TV rights Telenovela”.
[5] See: Map of deals and transactions updated until 10 March 2015.
[6] See: Map of deals
and transactions updated until 10 March 2015.
[7] Transfermarkt
- Josuha Guilavogui.
[8] The original minimum
return of €5.5 million set in September 2013 was increased every year by
€500.000 until 1 September 2015, since Doyen continued to own 50% of the
Guilavogui’s economic rights.
[9] The players
concerned were Roberto Canella Suárez, Álvaro Bustos Sandoval, Alejandro
Serrano García, Abdou Karim Tima, Mendy Formose, Juan Muñiz Gallego, Sergio
Álvarez Díaz, Óscar Guido Trejo and David Barral Torres.
[10] In the first phase,
Doyen receives a percentage of 50% of the economic rights of the nine players
until Doyen received an amount of €5 million for the transfer of one or more of
those players. After Doyen receives its first €5 million, Doyen’s ownership of
the economic rights of the remaining players is to be reduced to 40% until
Doyen received an additional €1 million. Once Doyen receives this additional €1
million, Doyen’s ownership of the economic rights of the remaining players
would be reduced to 30% until Doyen again receives €1 million from the selling
of those players. Consequently, the agreement stipulates that Doyen is to
receive an amount equal or superior to €7 million for the transfer of players
in which it partly owned the economic rights.
[11] As an exception,
Doyen only gets 10% of the economic rights of the players Alberto Botía and
Miguel de las Cuevas.
[12] Moreover, the 20% of the transfer fee for De las Cuevas that Sporting owed Doyen consisted of 10% for the
economic rights and 10% as an agency fee.
[13] This figure might
even get higher when taking into account that Doyen had a share in all Sporting
de Gijón players and the fact that Pedro León is still registered as a Getafe
player.
[14] With seven matches
to go, Sporting finds itself in 17th place.